Nevi and Birthmarks
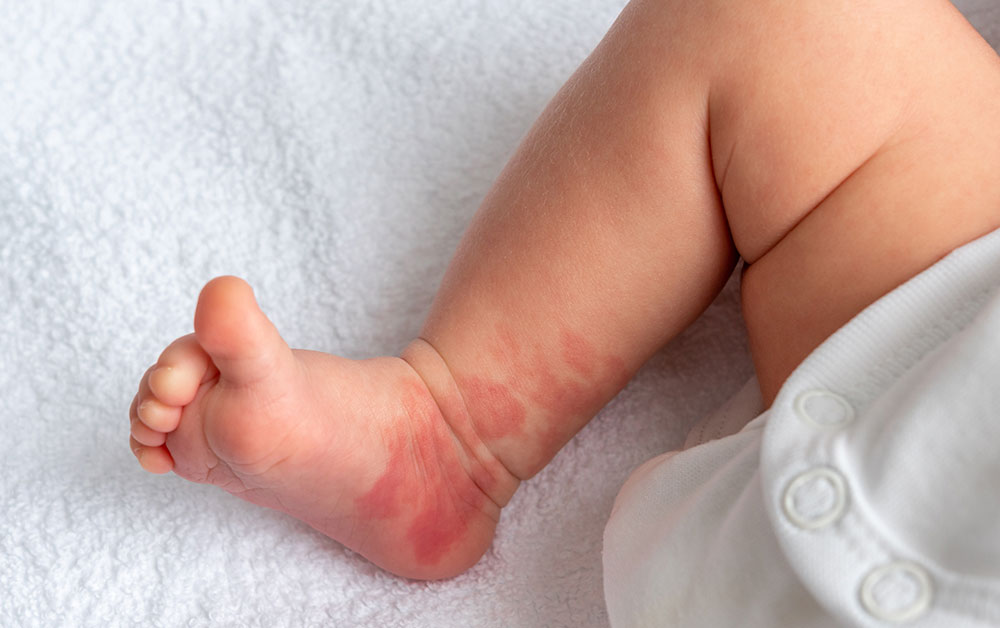
A spot that is present on the skin at birth or that appears shortly thereafter is called a birthmark. Birthmarks can be red, purple, brown or black. They can be large and small.
Pigmented birthmarks include moles (congenital nevi), mongolian spots and café au lait spots. These result from increased pigment in the skin and tend to be tan, brown or black.
Vascular birthmarks can be pink, red or purple as a result of increased blood vessels in the skin. These include hemangiomas, port wine stains and salmon colored patches.
When should birthmarks be removed?
Most birthmarks are harmless and do not require any treatment. However, the American Academy of Dermatology does encourage concerned parents of newborns with birthmarks to consult a dermatologist to rule out any medical conditions that could complicate the child’s health.
Birthmark removal can be done for both medical and cosmetic reasons. If a birthmark is large and/or is in a highly visible area such as the face, removal might be considered in the interest of emotional and psychological well-being.
What is a nevi?
A nevus, often called a mole, is a growth on the skin that develops when pigment cells (melanocytes) grow in clusters. Most adults have between 10 and 40 nevi. Although moles may be present at birth, they usually appear later in childhood. Most people continue to develop new moles until about age 40.
What does a nevus look like?
A common nevus is round or oval, with a smooth surface, and a distinct edge. A nevus usually has an even color of pink, tan or brown and will be either dome shaped or flat.
Can a benign nevus turn into melanoma?
Yes, but this is rare. Most moles remain stable over time. Call your dermatologist if you notice growth, changes or symptoms at the site of any of your moles.
What is a dysplastic nevus?
There is an entire spectrum of mole/nevi characteristics. At one end of the spectrum are regular benign nevi and at the other end is melanoma. In between, there are dysplastic nevi. If a nevus appears atypical or irregular during your skin check, a biopsy will be performed and this specimen is evaluated microscopically.
A dysplastic nevus is often graded as mild, moderate or severely dysplastic. The moderate and severely dysplastic nevi fall closest on that spectrum to melanoma and complete removal of these lesions is typically recommended.
Researchers estimate that the chance of melanoma is about ten times greater for someone with more than five dysplastic nevi than for someone who has none.
Should I get this mole checked?
Call your dermatologist if you notice any of the following changes in any of your moles:
- The color changes
- The mole gets unevenly smaller or bigger (unlike normal moles in children, which get evenly bigger as a child grows)
- The mole changes in shape, texture or height
- The skin on the surface becomes dry or scaly
- The mole becomes hard or feels lumpy
- It starts to itch
- It bleeds or oozes