Psoriasis
What is Psoriasis?
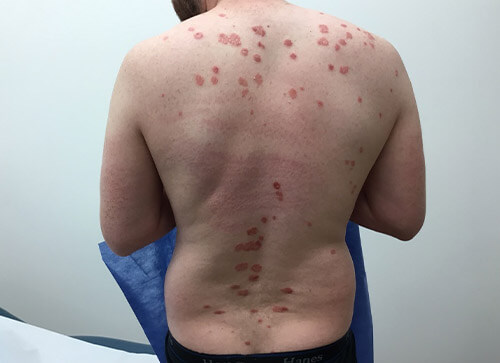
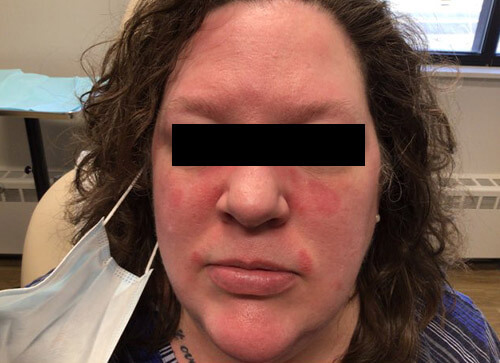
Psoriasis is a common skin condition that causes red, raised, dry patches to appear on the skin. Psoriasis can be chronic, and can come and go throughout your lifetime.
What are the symptoms of psoriasis?
Most patients with psoriasis note red, raised patches on their elbows and knees, but they can appear anywhere on the skin surface. Some patients with psoriasis complain of itching and stinging sensations, but many have no skin discomfort at all.
Approximately 10 to 20% of patients with skin psoriasis also experience joint aches and pains (psoriatic arthritis).
Many patients with psoriasis feel very self-conscious about their appearance; they might try to cover up the affected areas or avoid situations where their skin might be shown. Appropriate treatment of psoriasis can reduce inflammation and relieve the symptoms of this condition.
What causes psoriasis?
Psoriasis is caused by inflammation in the skin that results in a buildup of abnormally fast growing skin cells; this results in the characteristic thick, scaly patches. We do not know the exact cause of this skin inflammation, but we do know that both genetics and the immune system play a role. Many patients with psoriasis will note that they have relatives affected by this disorder as well.
Psoriasis is not contagious, you cannot ‘catch’ psoriasis from someone else, nor can someone else ‘catch’ psoriasis from you.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
Psoriasis is often diagnosed by visual examination of the skin by a dermatologist. Your dermatologist might also take a piece of skin (a biopsy) for evaluation under a microscope. Under the microscope the skin of psoriasis will look thicker and more inflamed when compared to normal skin or skin with eczema.
Evaluation by your dermatologist will help determine the severity of your psoriasis (the amount of body surface area involved) and any other associated symptoms. This information will help determine the best treatment options for you.
How is psoriasis treated?
A number of therapies are available for treating psoriasis. Topical treatments (creams, ointments, shampoos) are usually used in the treatment of mild psoriasis. Treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis (psoriasis that covers a larger body surface area) typically involves a combination therapy. In addition to topical agents, your dermatologist might prescribe phototherapy (also called light therapy) and/or systemic medications including biologic drugs.
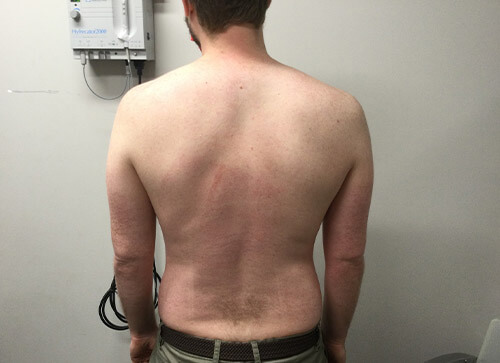
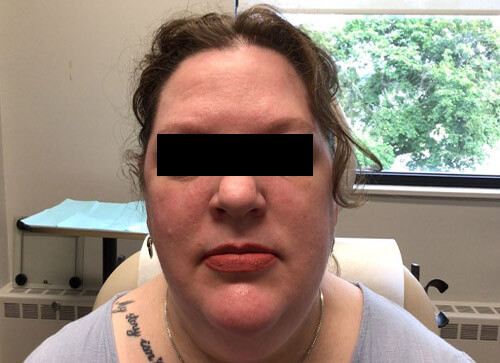
In our practice, we use all available treatment modalities to individualize a treatment plan that is right for each of our psoriasis patients. In addition to topical or systemic medications, we might also recommend use of our Xtrac laser to treat stubborn psoriasis patches. Most insurance carriers typically cover all of these treatment options.
What are biologic drugs?
Perhaps you have seen television commercials for drugs such as Enbrel, Humira, Stelara, Cosentyx, or Taltz and their successful use in treating psoriasis. These are examples of the biologic drugs (or biologics). Biologics are used in the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. These medications are given by a subcutaneous injection. They are called biologics because they are derived from living cells cultured in a laboratory. Biologics are unique compared to more traditional systemic drugs because they have a more targeted effect on the immune system rather than affecting the entire immune system.
Completely clear skin is possible with biologic therapy. In our office, we have had many unbelievable successes with this newer treatment option for psoriasis.